Excessive alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on a person’s health, both in the short-term and in the long-term. In fact, it has been linked to a wide range of health issues, including heart disease, stroke, liver disease, and cancer.
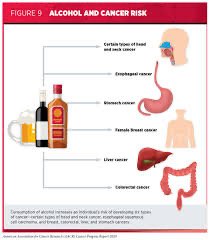
The consumption of alcohol over an extended period of time can weaken the immune system, impair memory, and cause various brain disorders. Notably, both alcohol and its metabolite acetaldehyde have been classified as Group 1 carcinogens, which are agents that cause cancer. Additionally, alcohol consumption is also considered a risk factor for mouth, pharynx, larynx, oesophagus, breast, bowel, and liver cancers.
One of the many ways in which alcohol harms the body is by causing gut health issues. The gut microbiome, which consists of trillions of bacteria that reside in the gastrointestinal tract, plays a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function. When a person consumes excessive amounts of alcohol, it can disrupt the balance of bacteria in the gut microbiome, leading to the production of more harmful than healthy bacteria. This, in turn, can cause digestive troubles like bloating, gas, leaky gut, loose motions, and other issues.
It is essential to note that alcohol consumption affects different people in different ways, and the amount and frequency of alcohol consumption that can cause harm to an individual can vary. Moreover, it is crucial to understand that even moderate consumption of alcohol can have adverse effects on health, especially in the long term.
Therefore, it is important to limit alcohol consumption to safe levels and maintain a healthy lifestyle to prevent any adverse health effects associated with excessive alcohol consumption. This can be achieved by consuming alcohol in moderation, staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and getting enough sleep and exercise. If a person is struggling with alcohol addiction, seeking professional help and support can also be beneficial in achieving a healthier lifestyle.